How Much Do You Know About "Cascadia Subduction Zone: Seismic Hazard, Tsunami Risk, And Scientific Research"?
Editor's Notes: "Cascadia Subduction Zone: Seismic Hazard, Tsunami Risk, And Scientific Research" have published today, May 12, 2023. This topic is important to read because it provides information about the risks associated with the Cascadia Subduction Zone, and what steps can be taken to mitigate these risks.
After some analysis and digging, we made this "Cascadia Subduction Zone: Seismic Hazard, Tsunami Risk, And Scientific Research" guide to help you make right decision.
| Key Differences | Seismic Hazard | Tsunami Risk | Scientific Research |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Cascadia Subduction Zone | Cascadia Subduction Zone | Cascadia Subduction Zone |
| Type of Hazard | Earthquake | Tsunami | Studies to understand the nature of the risks |
| Potential Impact | Devastating | Devastating | Improved understanding and preparedness |
Below the main article topics to learn more about "Cascadia Subduction Zone: Seismic Hazard, Tsunami Risk, And Scientific Research".
FAQ
This FAQ section aims to address common queries and dispel misconceptions regarding the Cascadia Subduction Zone's seismic hazard, tsunami risk, and scientific research.
Question 1: What poses the greatest seismic hazard in the Pacific Northwest?
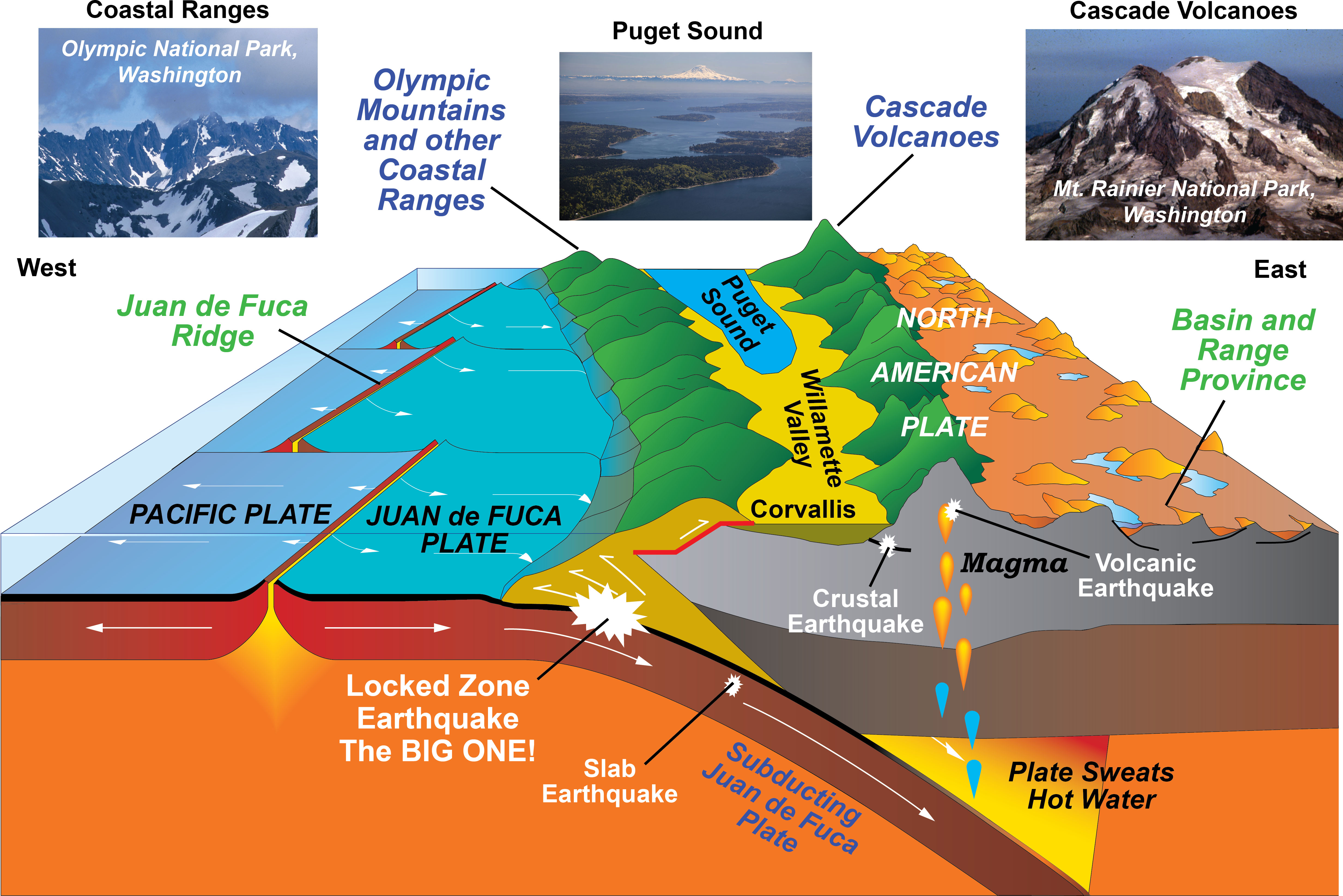
The Cascadia Subduction Zone, where the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate is thrusting beneath the North American plate, presents the most significant seismic hazard for the Pacific Northwest. The accumulation of strain along this interface can culminate in major earthquakes.
Question 2: What is the likelihood of a large earthquake occurring in the Cascadia Subduction Zone?
Paleoseismological evidence suggests that large earthquakes (magnitude 8-9) have occurred in the Cascadia Subduction Zone on average every 500 to 600 years. The last such event occurred approximately 300 years ago, indicating that the region is overdue for a major earthquake.
Question 3: How can we prepare for a potential earthquake and tsunami?
Efforts should focus on promoting earthquake awareness and preparedness, including developing and implementing emergency plans, participating in drills, and securing homes and infrastructure. Tsunami preparedness involves establishing evacuation routes and mustering points in vulnerable coastal areas.
Question 4: What tools do scientists use to monitor the Cascadia Subduction Zone?
Scientists employ a range of monitoring instruments, including seismic networks, GPS arrays, and tide gauges. These tools provide data on earthquake activity, crustal deformation, and sea-level changes, aiding in hazard assessment and forecasting.
Convergent Plate Boundaries—Subduction Zones - Geology (U.S. National - Source www.nps.gov
Question 5: How does research contribute to our understanding of the Cascadia Subduction Zone?
Scientific research plays a vital role in advancing our knowledge of the Cascadia Subduction Zone. Studies on past earthquakes, crustal structure, and plate interactions enhance our understanding of the system's behavior. Research also informs hazard modeling and risk assessment, leading to more effective mitigation strategies.
Question 6: What can individuals do to further scientific research and public education?
Individuals can support scientific research by participating in citizen science programs, providing data from personal seismic sensors, and advocating for funding initiatives. Public education can be promoted through volunteering with educational organizations and sharing accurate information about the Cascadia Subduction Zone and preparedness measures.
Overall, the Cascadia Subduction Zone poses a significant seismic and tsunami hazard, but through a combination of scientific research, hazard assessment, and community preparedness, the risks can be mitigated. Engaging in public education and supporting research efforts are crucial for safeguarding our communities and ensuring a resilient future.
Refer to the comprehensive article for further insight into the Cascadia Subduction Zone.
Tips
This detailed article on "Cascadia Subduction Zone: Seismic Hazard, Tsunami Risk, And Scientific Research" offers valuable tips to enhance understanding of the Cascadia subduction zone and its potential hazards:
Tip 1: Education and Awareness
Familiarize yourself with the seismic and tsunami risks associated with the Cascadia subduction zone. Participate in educational programs, read scientific reports, and stay informed about recent research and risk assessment studies.
Tip 2: Hazard Mapping and Planning
Identify areas at risk of ground shaking, liquefaction, landslides, and tsunami inundation. Use hazard maps to develop emergency plans, building codes, and land-use regulations that enhance community resilience.
Tip 3: Structural Reinforcement and Retrofitting
Take proactive measures to strengthen and retrofit homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure to withstand earthquake and tsunami forces. Implement seismic design features, elevate structures above potential flood levels, and ensure adequate bracing and anchoring.
Tip 4: Emergency Preparedness and Evacuation
Create a comprehensive emergency plan that includes evacuation routes, communication methods, and meeting places. Practice evacuation drills and prepare emergency kits with essential supplies.
Tip 5: Community Engagement and Collaboration
Foster partnerships between scientists, emergency managers, local governments, and community members. Encourage collaboration on risk assessment, preparedness strategies, and public education initiatives.
By following these tips, you can contribute to building a safer and more resilient society that is prepared to respond effectively to the potential hazards associated with the Cascadia subduction zone.
Cascadia Subduction Zone: Seismic Hazard, Tsunami Risk, And Scientific Research
The Cascadia Subduction Zone presents a significant seismic hazard, tsunami risk, and serves as a focal point for scientific research. Delving into the various dimensions of these aspects yields a comprehensive understanding of their significance:
- Subduction Zone: Plate convergence zone with potential for major earthquakes.
- Seismic Hazard: High risk of large-magnitude earthquakes with far-reaching effects.
- Tsunami Risk: Earthquakes can trigger devastating tsunamis, impacting coastal communities.
- Scientific Research: Studying the zone aids in understanding earthquake and tsunami dynamics.
- Hazard Mitigation: Research informs preparedness measures, reducing the impact of future events.
- Community Resilience: Public awareness and education are crucial for disaster preparedness.

cascadia-subduction-zone-map – Temblor.net - Source temblor.net
These aspects are interconnected, underscoring the importance of comprehensive hazard assessment and mitigation strategies. By understanding the nature of the Cascadia Subduction Zone, researchers and policymakers can develop effective measures to safeguard communities and infrastructure, while ongoing research contributes to a deeper understanding of earthquake and tsunami phenomena.
Cascadia Subduction Zone: Seismic Hazard, Tsunami Risk, And Scientific Research
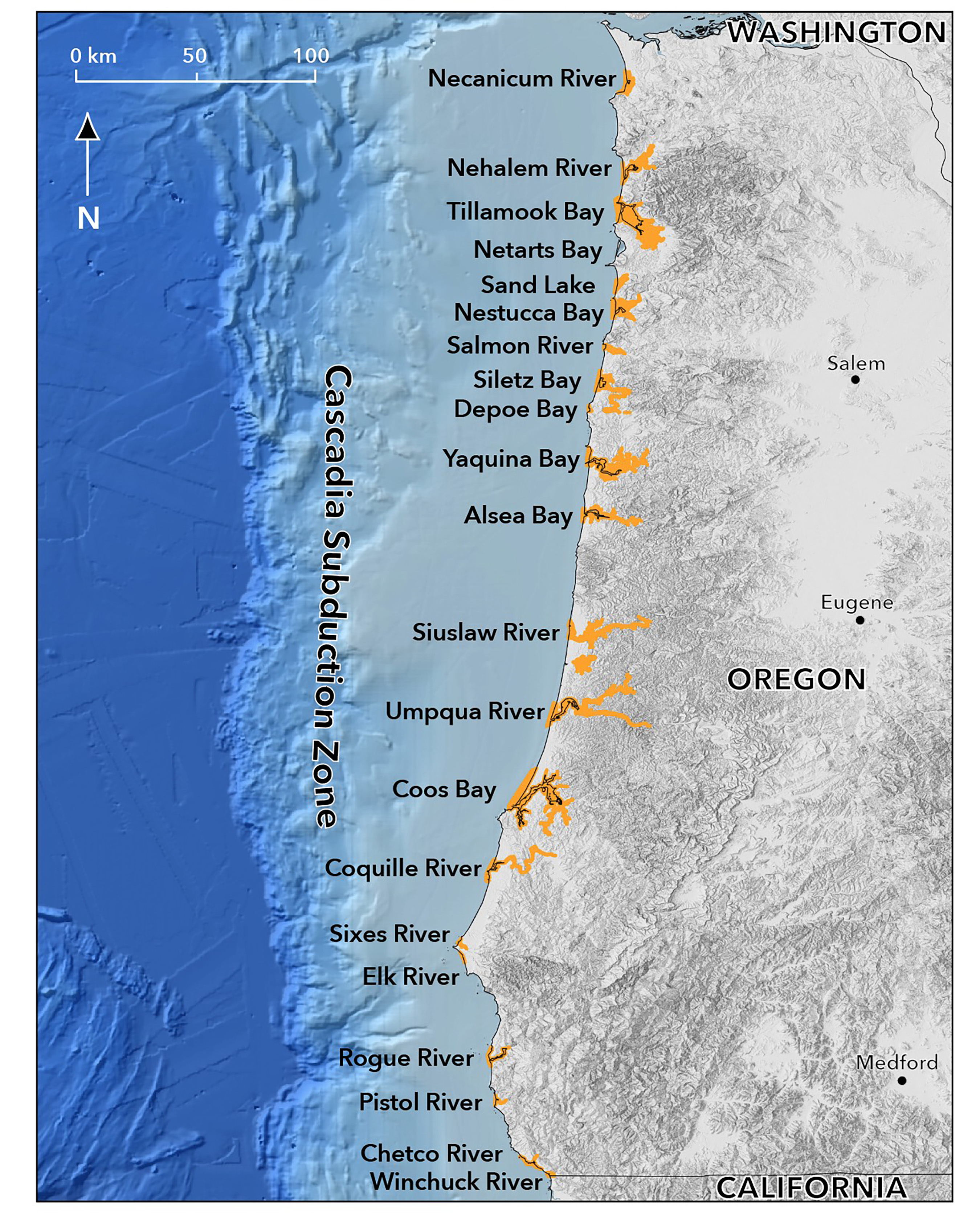
The Cascadia Subduction Zone (CSZ) is a 1,100-kilometer-long fault that stretches from northern California to southern British Columbia. It is the convergence boundary between the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate and the North American Plate. The CSZ is a major source of seismic and tsunami hazard for the Pacific Northwest.
Researchers prepare for the next earthquake in Oregon | Virginia Tech - Source news.vt.edu
Scientific research is essential for understanding the CSZ and mitigating the risks it poses. Scientists are using a variety of methods to study the CSZ, including seismic monitoring, GPS measurements, and paleoseismic trenching. This research has helped us to better understand the history of earthquakes and tsunamis in the Pacific Northwest, and to develop models that can predict future events.
The CSZ is a complex system, and there is still much that we do not know about it. However, the scientific research that has been conducted to date has provided us with valuable information that can help us to mitigate the risks that the CSZ poses to the Pacific Northwest.
| Seismic Hazard | Tsunami Risk | Scientific Research |
|---|---|---|
| The CSZ is a major source of seismic hazard for the Pacific Northwest. | The CSZ is also a major source of tsunami risk for the Pacific Northwest. | Seismic monitoring, GPS measurements, and paleoseismic trenching are used to study the CSZ. |
| The last major earthquake on the CSZ occurred in 1700. | A tsunami generated by a magnitude 9.0 earthquake on the CSZ could devastate the Pacific Northwest. | Scientific research has helped us to better understand the history of earthquakes and tsunamis in the Pacific Northwest. |
| The CSZ is expected to produce a major earthquake in the next 50 years. | The Pacific Northwest is not prepared for a major earthquake or tsunami. | Scientific research is essential for developing models that can predict future earthquakes and tsunamis. |
Conclusion
The CSZ is a major seismic and tsunami hazard for the Pacific Northwest. Scientific research is essential for understanding the CSZ and mitigating the risks it poses. The research that has been conducted to date has provided us with valuable information that can help us to prepare for future earthquakes and tsunamis. However, there is still much that we do not know about the CSZ, and continued research is needed to ensure the safety of the Pacific Northwest.
The CSZ is a reminder that we live in a dynamic and ever-changing world. We must be prepared for natural disasters, and scientific research is an essential tool for helping us to do so.